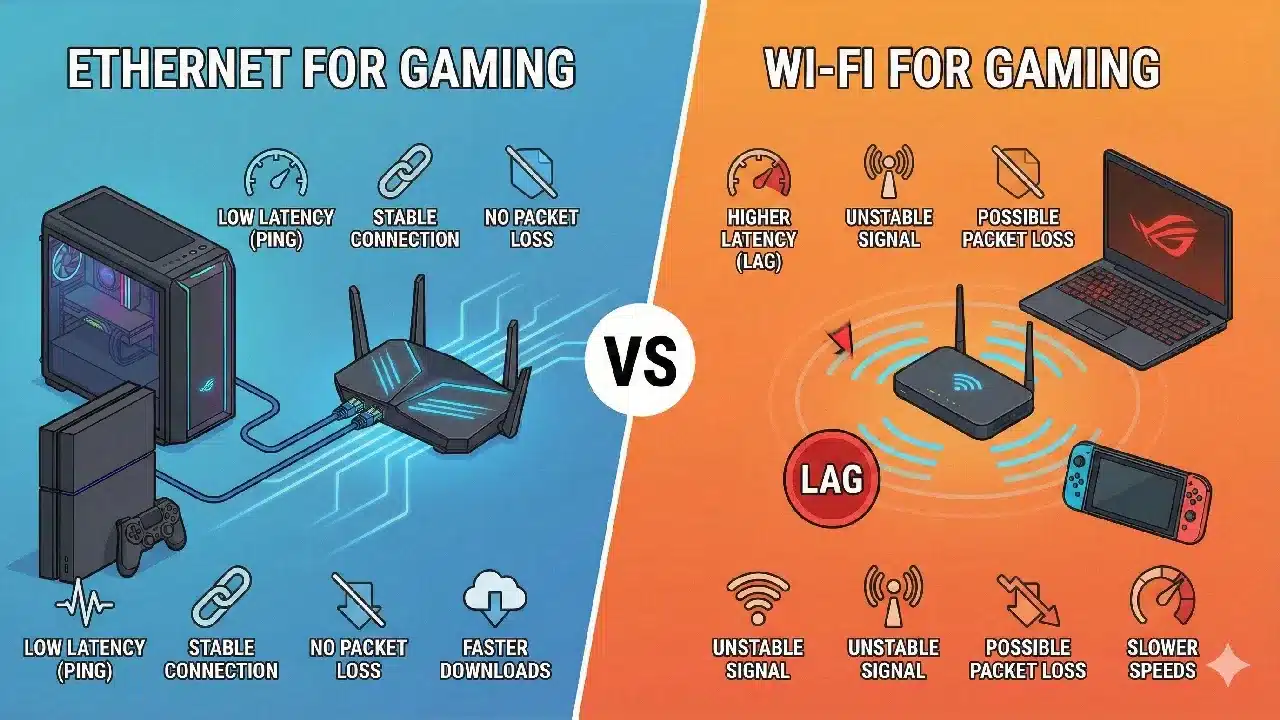
The Hidden Enemy of Online Gaming
When gamers complain about lag, rubber-banding, hit-registration issues, or random disconnects, they often blame the game servers, their PC, or even other players. But one of the most common and overlooked causes of poor online gaming performance is Wi-Fi.
While Wi-Fi is convenient, it is fundamentally worse than Ethernet for gaming in almost every technical way that matters: latency, stability, packet loss, and consistency. Even a fast Wi-Fi connection with high download speeds can perform poorly in games compared to a slower wired Ethernet connection.
This article explains why Wi-Fi struggles with gaming, how Ethernet solves those problems, and when Wi-Fi might still be acceptable.
🎮 What Online Games Actually Need (It’s Not Speed)
A common misconception is that gaming requires fast internet speeds. In reality:
-
Most online games use very little bandwidth
-
What matters most is latency, consistency, and reliability
What games really care about:
-
Low ping (latency)
-
Stable connection
-
Minimal packet loss
-
Consistent timing (low jitter)
Wi-Fi is bad at delivering consistency. Ethernet excels at it.
🔌 Ethernet vs Wi-Fi: The Core Difference
Ethernet
-
Direct wired connection
-
Dedicated, full-duplex communication
-
No interference
-
Extremely stable
-
Consistent latency
Wi-Fi
-
Wireless, shared medium
-
Half-duplex communication
-
Susceptible to interference
-
Variable latency
-
Unpredictable performance
This single difference — wired vs wireless — is why Ethernet is superior for gaming.
⏱️ Latency: The Biggest Problem With Wi-Fi
What is latency?
Latency (ping) is the time it takes for data to travel from your PC to the game server and back.
-
Lower latency = faster response
-
Higher latency = delayed actions
Ethernet latency
-
Very low and consistent
-
Usually 1–2 ms within your local network
-
Predictable timing
Wi-Fi latency
-
Higher and inconsistent
-
Can fluctuate from moment to moment
-
Adds extra processing delay
Even if your Wi-Fi shows “low ping” in speed tests, moment-to-moment spikes still happen — and games feel those spikes instantly.
📉 Jitter: Why Wi-Fi Feels Unstable
What is jitter?
Jitter is the variation in latency.
-
Stable ping: 20ms → 20ms → 20ms
-
High jitter: 20ms → 80ms → 30ms → 100ms
Games hate jitter.
Wi-Fi causes jitter because:
-
Devices compete for airtime
-
Signal strength fluctuates
-
Interference constantly changes
-
Data packets wait their turn
Ethernet delivers packets in a steady, predictable flow, which is why movement and aiming feel smoother.
📡 Interference: Wi-Fi’s Biggest Weakness
Wi-Fi signals travel through the air — and the air is crowded.
Common sources of Wi-Fi interference:
-
Other Wi-Fi networks (neighbors)
-
Bluetooth devices
-
Microwaves
-
Smart home devices
-
Baby monitors
-
Wireless headphones
-
Walls, floors, metal objects
Every interference source increases:
-
Packet delays
-
Packet loss
-
Latency spikes
Ethernet is immune to all of this because it uses a physical cable.
📦 Packet Loss: The Silent Game Killer
What is packet loss?
Packet loss happens when data packets never reach their destination.
In games, packet loss causes:
-
Rubber-banding
-
Teleporting players
-
Shots not registering
-
Random disconnects
Wi-Fi packet loss happens because:
-
Signal drops
-
Interference corrupts packets
-
Congestion causes packets to be dropped
Ethernet connections rarely experience packet loss unless there’s a serious network fault.
🎯 Why Wi-Fi Feels Worse in Competitive Games
Competitive games are extremely sensitive to network issues.
Games that suffer most on Wi-Fi:
-
Valorant
-
CS2
-
Fortnite
-
Apex Legends
-
Warzone
-
Rocket League
These games require:
-
Precise hit registration
-
Instant movement updates
-
Reliable server communication
Even tiny Wi-Fi spikes can mean:
-
Missed shots
-
Delayed inputs
-
Losing gunfights you should have won
That’s why almost all professional and competitive players use Ethernet.
🖥️ Bandwidth Sharing: Wi-Fi Is a Shared Resource
Wi-Fi works like a conversation where:
-
Only one device can “talk” at a time
-
Everyone must wait their turn
If someone in your house is:
-
Streaming video
-
Downloading files
-
Using cloud backups
-
On a video call
Your gaming packets must wait, causing lag.
Ethernet connections:
-
Have dedicated bandwidth
-
Do not compete with other devices on the same cable
-
Maintain stable performance under load
🕹️ Input Delay and “Laggy Feel”
Even when ping looks acceptable, Wi-Fi often feels worse.
Why?
-
Inconsistent packet timing
-
Micro-stutters in data flow
-
Variable delays between packets
This causes:
-
Input delay
-
Floaty movement
-
Inconsistent aim
Ethernet delivers predictable timing, which is crucial for muscle memory in gaming.
🔋 Power Saving and Wi-Fi Instability
Many Wi-Fi adapters use power-saving features:
-
Reducing transmit power
-
Sleeping between packets
-
Throttling activity
These features are great for battery life — terrible for gaming.
Ethernet adapters:
-
Run at full power constantly
-
No sleep states
-
No signal negotiation delays
📊 Speed Tests Lie (For Gaming)
Wi-Fi users often say:
“My Wi-Fi speed is fast — I get 300 Mbps!”
Speed tests measure:
-
Download bandwidth
-
Short bursts of data
Games care about:
-
Packet timing
-
Reliability
-
Latency consistency
You can have:
-
Fast Wi-Fi
-
Terrible gaming experience
Ethernet prioritizes quality over raw speed, which is exactly what games need.
🧠 Common Myths About Wi-Fi Gaming
❌ “Wi-Fi 6 / 6E fixes everything”
Wi-Fi 6 improves throughput and efficiency, but:
-
It’s still wireless
-
Still subject to interference
-
Still shared
It’s better — but still worse than Ethernet.
❌ “I don’t notice lag on Wi-Fi”
You might not notice it casually, but:
-
Competitive games expose it
-
High-skill play magnifies small delays
-
Once you switch to Ethernet, the difference is obvious
❌ “Ethernet is old technology”
Ethernet evolves too:
-
1GbE → 2.5GbE → 10GbE
-
Lower latency
-
Better reliability
Ethernet remains the gold standard for networking.
📏 When Wi-Fi Is Acceptable for Gaming
Wi-Fi can be okay if:
-
You play casual games
-
You’re far from competitive
-
Your router is close
-
Few devices share the network
-
You use modern Wi-Fi standards
-
Ethernet is physically impossible
But “acceptable” is not the same as “optimal”.
🛠️ How to Improve Wi-Fi Gaming (If Ethernet Isn’t Possible)
If you must use Wi-Fi:
-
Use the 5GHz or 6GHz band
-
Move closer to the router
-
Reduce interference
-
Upgrade your router
-
Use a quality Wi-Fi adapter
-
Disable power saving on the adapter
Even then, it still won’t match Ethernet.
🔌 Why Ethernet Always Wins for Gaming
Ethernet offers:
-
Lower latency
-
Near-zero jitter
-
Minimal packet loss
-
Stable, consistent performance
-
Immunity to interference
-
Better hit registration
-
Smoother movement
This is why:
-
LAN tournaments use Ethernet
-
Esports players use Ethernet
-
Competitive gamers recommend Ethernet